Editors’ Picks
Moderate-to-vigorous Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior Are Independently Associated With Renal Function: A Cross-sectional Study
Authors
Megumi Hara, Yuichiro Nishida, Keitaro Tanaka, Chisato Shimanoe, Kayoko Koga, Takuma Furukawa, Yasuki Higaki, Koichi Shinchi, Hiroaki Ikezaki, Masayuki Murata, Kenji Takeuchi, Takashi Tamura, Asahi Hishida, Mineko Tsukamoto, Yuka Kadomatsu, Keitaro Matsuo, Isao Oze, Haruo Mikami, Miho Kusakabe, Toshiro Takezaki, Rie Ibusuki, Sadao Suzuki, Hiroko Nakagawa-Senda, Daisuke Matsui, Teruhide Koyama, Kiyonori Kuriki, Naoyuki Takashima, Yasuyuki Nakamura, Kokichi Arisawa, Sakurako Katsuura-Kamano, Kenji Wakai
J-Stage
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jea/33/6/33_JE20210155/_article
Highlights
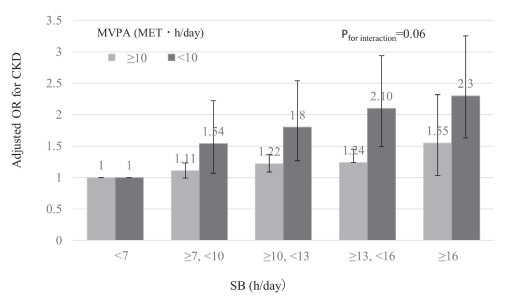
- Insufficient moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) and longer sedentary behavior (SB) are independently associated with lower renal function and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
- Significant interactions between sex and MVPA were detected for CKD.
- Replacing 1 hour of SB with 1 hour of physical activity was estimated to lead to 3% to 4% lower odds ratio of CKD.
Selected Result