Editors’ Picks
Rural-urban Disparities in the Prevalence of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia in Taiwan: A Door-to-door Nationwide Study
Authors
Chih-Ching Liu, Chien-Hui Liu, Yu Sun, Huey-Jane Lee, Li-Yu Tang, Ming-Jang Chiu
J-Stage
Highlights
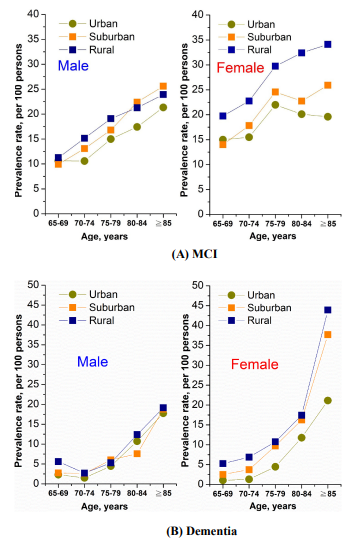
- This nationwide, door-to-door survey demonstrated significantly higher prevalence of dementia in rural areas with rural/urban ratio being 1.9, and the urbanization effects were more significant in women with the ratio up to more than 5 in women at the age of 65-74 years.
- Urbanization level was an independent associated factor for mild cognitive impairment and dementia.
- Impacts of factors such as sex and regular exercise on dementia varied among different urbanization status.
- Because of the inequality of medical services between urbanization levels, interventions of dementia prevention specifically for rural or urban residents are suggested in future public health policy.
Selected Result